How to interpret the classes of tightness and their significance for security?
Ingress Protection Classes
Almost all devices have an assigned IP code that defines the conditions under which their use is safe. The designation of the IP ingress protection class is particularly important for outdoor devices, such as gate drives or surveillance cameras. Familiarize yourself with how to interpret the IP ingress protection class code and what it specifically means.

What is the IP ingress protection class?
This is a parameter often used not only in surveillance systems but also in many other electronic devices. Many buyers wonder about the meaning of terms such as "ingress protection class" or "water resistance" when shopping. Although this issue may seem complex, it is actually relatively easy to understand. It is enough to familiarize yourself with a few key values to effectively choose the right equipment.
The protection class, also known as IP (International Protection Rating), is an indicator that specifies whether a device is protected against the penetration of unwanted solid objects and moisture. In other words, it shows whether the device is hermetic and to what extent. The IP ingress protection class is mainly used to mark electronic devices such as smartphones, watches, cameras, or video intercoms, but its application extends much further. The IP ingress protection class is used to classify items used outdoors, which can be affected by weather conditions.
What do the numbers in the IP class mean?
The first number indicates the degree of protection of the device against the access of solid objects. This number also informs whether dangerous elements inside the device are adequately secured to be safe for users. The range of the first digit is from 0 to 6. The second number specifies how well the device is protected against water and moisture, which usually means the use of special seals. The second digit of this indicator ranges from 0 to 9.

| Digit | Description of the first digit: | Second digit. | Description of the second digit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | No protection. | 0 | No protection. |
| 1 | Protection against the ingress of solid objects larger than 50 mm. | 1 | Resistant to vertically falling water droplets. |
| 2 | Protection against the ingress of solid objects larger than 12.5 mm. | 2 | Resistant to droplets falling at an angle of 15 degrees. |
| 3 | Protection against the ingress of solid objects larger than 2.5 mm. | 3 | Resistant to droplets falling at an angle of 60 degrees. |
| 4 | Protection against the ingress of solid objects larger than 1 mm. | 4 | Protection against water droplets falling from all directions. |
| 5 | Dustproof. | 5 | Protection against water jets from all directions. |
| 6 | Dust-tight. | 6 | Water wave - strong jets from any direction. |
| x | x | 7 | Device is waterproof when submerged (30 minutes at a depth of 0.15m above the top of the enclosure or 1m above the bottom for enclosures lower than 0.85m). |
| x | x | 8 | Device is waterproof under continuous immersion and increased pressure. |
| x | x | 9 | Protection against water jets from all directions. (according to the German standard DIN 40050) |
It is also worth focusing a bit more on the first and second digits and describing them in detail.
- First digit:
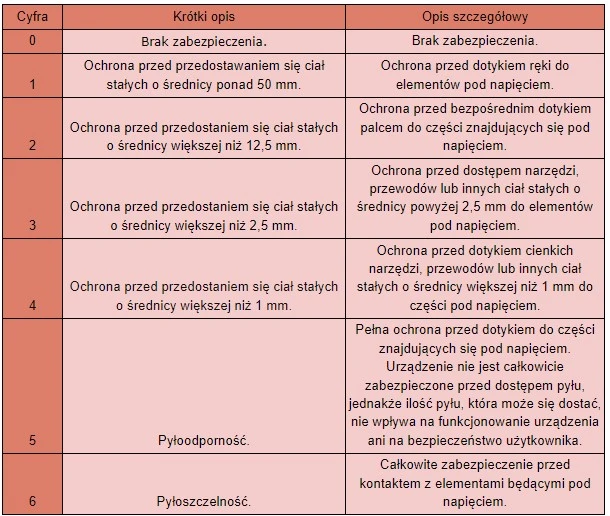
| Digit | Short description | Detailed description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No protection. | No protection. |
| 1 | Protection against the ingress of solid objects larger than 50 mm. | Protection against hand contact with live parts. |
| 2 | Protection against the ingress of solid objects larger than 12.5 mm. | Protection against direct finger contact with live parts. |
| 3 | Protection against the ingress of solid objects larger than 2.5 mm. | Protection against access of tools, wires, or other solid objects larger than 2.5 mm to live parts. |
| 4 | Protection against the ingress of solid objects larger than 1 mm. | Protection against contact with thin tools, wires, or other solid objects larger than 1 mm with live parts. |
| 5 | Dustproof. | Full protection against contact with live parts. The device is not completely protected against dust ingress, however, the amount of dust that can enter the device does not affect its operation and user safety. |
| 6 | Dust-tight. | Complete protection against contact with live parts. |
- Second digit:
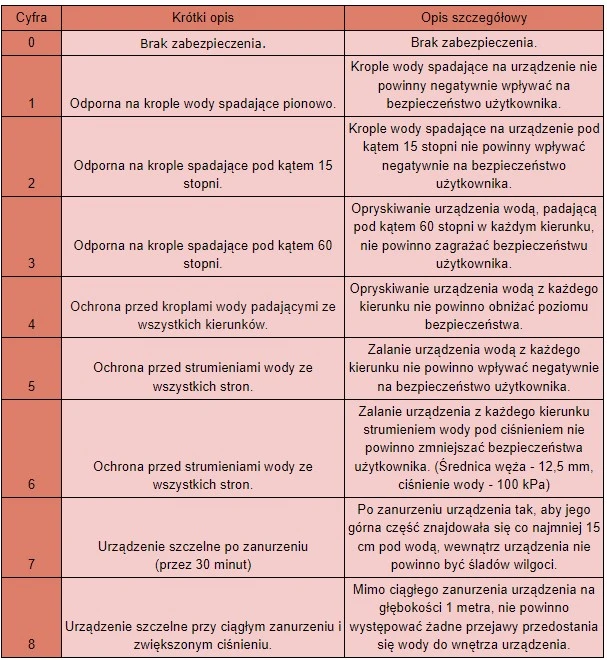
| Digit | Short description | Detailed description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No protection. | No protection. |
| 1 | Resistant to vertically falling water droplets. | Water droplets falling on the device should not negatively affect user safety. |
| 2 | Resistant to droplets falling at an angle of 15 degrees. | Water droplets falling on the device at an angle of 15 degrees should not negatively affect user safety. |
| 3 | Resistant to droplets falling at an angle of 60 degrees. | Spraying the device with water falling at an angle of 60 degrees in any direction should not threaten user safety. |
| 4 | Protection against water droplets falling from all directions. | Spraying the device with water from any direction should not lower the level of safety. |
| 5 | Protection against water jets from all sides. | Soaking the device with water from any direction should not negatively affect user safety. |
| 6 | Protection against water jets from all sides. | Soaking the device from any direction with a water jet under pressure should not reduce user safety. (Hose diameter - 12.5 mm, water pressure - 100 kPa) |
| 7 | Device is waterproof when submerged (for 30 minutes) | After submerging the device so that its top is 15 cm underwater, no water should enter the device. |
| 8 | Device is waterproof under continuous immersion and increased pressure. | Despite continuous immersion of the device at a depth of 1 meter, no water should enter the device. |
Example ingress protection classes:
- IP20 - an indicator that indicates limited ingress protection. This means that devices with this designation are protected against access by foreign solid objects larger than 50 mm, but do not offer protection against moisture.
- IP44 - an indicator providing the minimum ingress protection standard, suitable for outdoor devices such as surveillance cameras. It indicates that the device's enclosure is resistant to solid objects larger than 1 mm and provides protection against light rain.
- IP54 - this indicator indicates that the device's enclosure provides protection against solid objects of at least 1 mm in diameter and against rain. This is sufficient for applications such as gate drives.
- IP55 - indicates a high level of protection against dust (though not complete dust-tightness) and comprehensive protection against moisture. Devices with this indicator should be additionally protected when exposed to heavy rain.
- IP65 - this level of ingress protection guarantees dust-tightness (complete protection) and secures the device's enclosure against access to dangerous parts using wire. In terms of moisture, IP65 means resistance to heavy rain, making it suitable for outdoor use in harsh conditions.
- IP66 - this indicator is used for devices providing the highest level of protection, such as advanced gate drives or home surveillance systems. It offers dust-tightness and protection against heavy rain, making it ideal for outdoor use.
- IP67 - indicates complete dust resistance and the ability to withstand short-term immersion in water. The device can be submerged for up to 30 minutes at a depth of up to 15 cm above the top edge of the enclosure or up to 1 m above the bottom edge for enclosures lower than 0.85 m. With this ingress protection class, you can, for example, swim with your phone just below the water's surface.
What do the additional and supplementary letters in ingress protection ratings mean?
1. Additional letters in water resistance ratings:
M – this designation indicates that the device has been tested for resistance to harmful effects of water ingress, with tests conducted while the device's moving parts are in operation.
S – this symbol indicates that the machine has been tested for harmful effects of water ingress, assuming that the device's moving parts remain stationary during the test.
Additional protections for ingress protection classes.
In addition to having a specific ingress protection class in the purchased equipment, it is also worth considering additional protective measures to better secure the device, such as a camera, against unwanted surges or flooding.
1. Insulation of electrical wires.
Properly executed insulation of electrical wires is crucial to prevent unwanted electric charge flow outside the designated conductive element. This task is typically entrusted to qualified electricians, for whom the process of insulating wires is relatively simple. A key aspect during these activities is the selection of the appropriate material, which has low electrical conductivity.What materials to use?
- insulation tape:
Insulation tape is a relatively inexpensive material, making it very popular in the Polish market. It is primarily used for quick insulation of wires in case of any damage, even the smallest. Additionally, if necessary, insulation tape can be used to reinforce previously made connections or to mask cable clusters.

- heat shrink tubing:
Heat shrink tubing, although it may be harder to obtain, offers users rich functionality. It is valued for the ability to create very durable and solid insulation, effectively protecting wires from all kinds of damage. The popularity of this material among users stems from its high effectiveness. It is important that the heat shrink tubing is properly applied, which significantly improves the aesthetics of the cable itself.
When insulating electrical wires, it is important to pay attention to several key aspects. Users using insulation tape should carefully select its length and width. Insulation tapes are also available in various colors, which can help in identifying specific wires. Individuals without much experience should seek help from qualified electricians or experienced sellers. Attempts to insulate wires independently can lead to improper insulation, which in turn can result in electric shock, mechanical damage, or exposure of wires to moisture.
2. Insulating wiring from water.
The electrical installation in a building should be constructed to ensure maximum safety for users and increased resistance to damage, minimizing the risk of dangerous electric shocks. For underground installations, it is recommended to use protective conduits that protect wires from mechanical damage and environmental impact. Inside buildings, it is important that cables are completely insulated from contact with water.
Electrical wires should be installed close to the ceiling, while electrical outlets should be mounted high above the floor level to minimize the risk of contact with water. It is also important that all electrical equipment meets the minimum requirements for the IP protection class, which will provide adequate protection against external factors. It is also recommended to use robust protections that can automatically disconnect power in critical situations, increasing user safety. Such precautions are particularly important in buildings inhabited by children and the elderly, as well as in areas with increased humidity.
The risk of flooding can be effectively minimized by following a few key principles:
- Using waterproof equipment, which includes the appropriate selection of sockets, plugs, and cables, made by experienced professionals.
- Choosing electrical devices with an IP protection class ideally suited to the prevailing conditions, which increases their resistance to moisture.
- Using lower voltages, which can reduce the risk of serious damage in case of contact with water.
One should also not forget about daily precautions, such as being particularly careful when using electrical devices in places where they may come into contact with water or be flooded.
Mechanical protection class. What is IK and how can it help us fight vandalism?
IK is a scale that defines the mechanical strength of devices, defined in the European standard EN 62262 and its international counterpart IEC 62262:2002. This parameter indicates how resistant devices are to impacts and other external mechanical damage, which is often referred to as vandal resistance. The IK scale is widely used, among others, in surveillance cameras and other devices mounted externally, such as intercoms.
 Thanks to the IK designation, which informs about mechanical strength, when purchasing new equipment, one can precisely determine its suitability depending on the installation location. This designation consists of the letters IK and two digits that indicate the position on an 11-point scale (from "00" to "10"). A higher numerical value of the IK parameter indicates better mechanical strength. For example, by choosing a device with a high IK class, we can protect ourselves from additional costs and the need for replacement in case of damage by a vandal, especially when it is mounted outside the building. A key issue is also the material from which the device's enclosure is made. Polycarbonate (PC) and fiberglass-reinforced polycarbonate (PC+glass) are the most highly valued, offering the best durability. Enclosures made of ABS, GRP (glass-fiber reinforced polymer), and aluminum have slightly lower ratings. These materials, while still solid, may offer somewhat less resistance compared to polycarbonate.
Thanks to the IK designation, which informs about mechanical strength, when purchasing new equipment, one can precisely determine its suitability depending on the installation location. This designation consists of the letters IK and two digits that indicate the position on an 11-point scale (from "00" to "10"). A higher numerical value of the IK parameter indicates better mechanical strength. For example, by choosing a device with a high IK class, we can protect ourselves from additional costs and the need for replacement in case of damage by a vandal, especially when it is mounted outside the building. A key issue is also the material from which the device's enclosure is made. Polycarbonate (PC) and fiberglass-reinforced polycarbonate (PC+glass) are the most highly valued, offering the best durability. Enclosures made of ABS, GRP (glass-fiber reinforced polymer), and aluminum have slightly lower ratings. These materials, while still solid, may offer somewhat less resistance compared to polycarbonate.
| IK Level | Impact Energy | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No protection and resistance to impacts | No protection against impacts |
| 1 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 0.15 J | Impact with a light hammer |
| 2 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 0.20 J | Impact with a light hammer |
| 3 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 0.35 J | Impact with a light hammer |
| 4 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 0.50 J | Impact with a light hammer |
| 5 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 0.70 J | Impact with a light hammer |
| 6 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 1 J | Impact with a hammer weighing 0.5 kg from a height of 20 cm |
| 7 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 2 J | Impact with a hammer weighing 0.5 kg from a height of 40 cm |
| 8 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 5 J | Impact with a hammer weighing 1.7 kg from a height of 29.5 cm |
| 9 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 10 J | Impact with a hammer weighing 5 kg from a height of 20 cm |
| 10 | Protection and resistance to impacts of energy 20 J | Impact with a hammer weighing 5 kg from a height of 40 cm |
Is it worth worrying about?
If you want to be sure that cameras and other outdoor equipment are not damaged, you must consider that this equipment will be somewhat exposed to external factors. Therefore, before making a choice, check the ingress protection classes. Consider not only how the camera works but also the safety of the product.
Other articles
Brands zone
Our recommendations
- City monitoring
- Home monitoring
- Estate monitoring
- Shop monitoring
- Pharmacy monitoring
- Parking monitoring
- Office monitoring
- School monitoring
- Warehouse monitoring
- Gas station monitoring
- Hard drive capacity calculator
- Lens focal length calculator
- Comprehensive expert support
- Efficient order processing
- Competitive prices, promotions, and discounts
- 17 years on the market


















